By SABRINA KARL, Investopedia
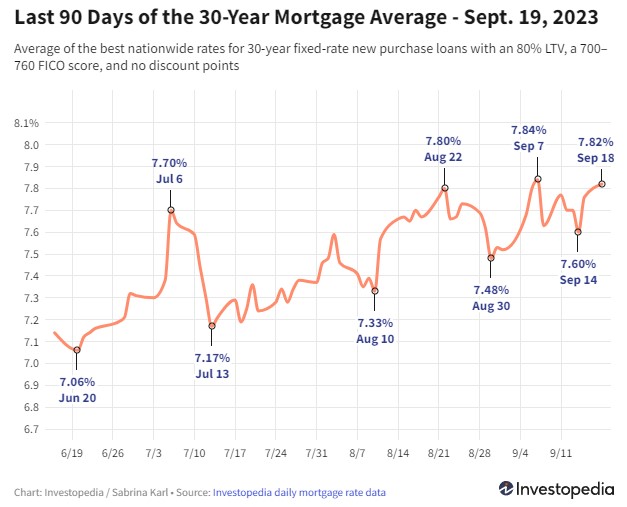
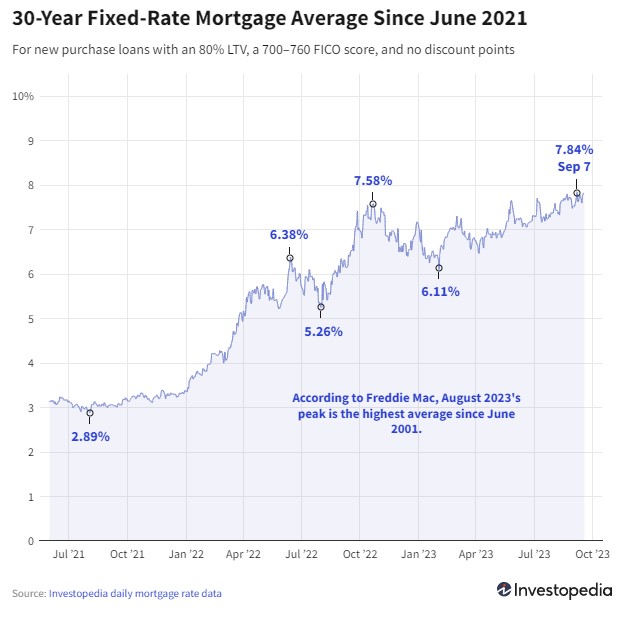
Rates on 30-year mortgages rose again Monday, adding to the jump they saw Friday and pushing the flagship average almost back to the historic 22-year high it registered earlier this month. Averages for most other loan types were flat to mildly up Monday, with only a couple of averages declining.Rates on 30-year new purchase mortgages gained 6 basis points Monday, after jumping 16 basis points Friday. That raises the 30-year average to 7.82%, which is just barely below Sept. 7's historic reading of 7.84%—its highest mark since 2001.
Monday rates on 15-year loans rose only a minor 2 basis points, nudging the average to 7.15%. Like 30-year rates, the 15-year average is now back within a couple of basis points of its recent peak—a 21-year high of 7.17% reached in mid-August.
Jumbo 30-year rates held steady for a second day Monday, at the average's high-water mark of 7.02%. Though daily jumbo averages are not available before 2009, it's reasonable to assume that August's peak average of 7.02% was the most expensive level reached for jumbo 30-year loans in at least 20 years.The biggest climbers Monday were the FHA 30-year and VA 30-year averages, each of which gained 12 basis points, while the FHA 15-year average sank 11 basis points. The only other average to decline was a minor dip of 3 basis points for the 7/6 ARM average.
What Causes Mortgage Rates to Rise or Fall?
Mortgage rates are determined by a complex interaction of macroeconomic and industry factors, such as:
- The level and direction of the bond market, especially 10-year Treasury yields
- The Federal Reserve's current monetary policy, especially as it relates to bond buying and funding government-backed mortgages
- Competition between mortgage lenders and across loan types
But starting in Nov. 2021, the Fed began tapering its bond purchases downward, making sizable reductions each month until reaching net-zero in March 2022.2
Since that time, the Fed has been aggressively raising the federal funds rate to fight decades-high inflation. While the fed funds rate can influence mortgage rates, it does not directly do so. In fact, the fed funds rate and mortgage rates can move in opposite directions.
However, given the historic speed and magnitude of the Fed's 2022 and 2023 rate increases—raising the benchmark rate a cumulative 5.25% over the last 18 months—even the indirect influence of the fed funds rate has resulted in an upward impact on mortgage rates over the last two years.
The Fed's next rate-setting meeting is scheduled to conclude Sept. 20, and financial markets have priced in a near-certainty that the central bank will hold rates steady this time. A rate increase in November or December is still a possibility, however, with traders forecasting odds of 35-40% of an increase being announced at one of those meetings.
Comments
Post a Comment
Thanks for the comment. Will get back to you as soon as convenient, if necessary.